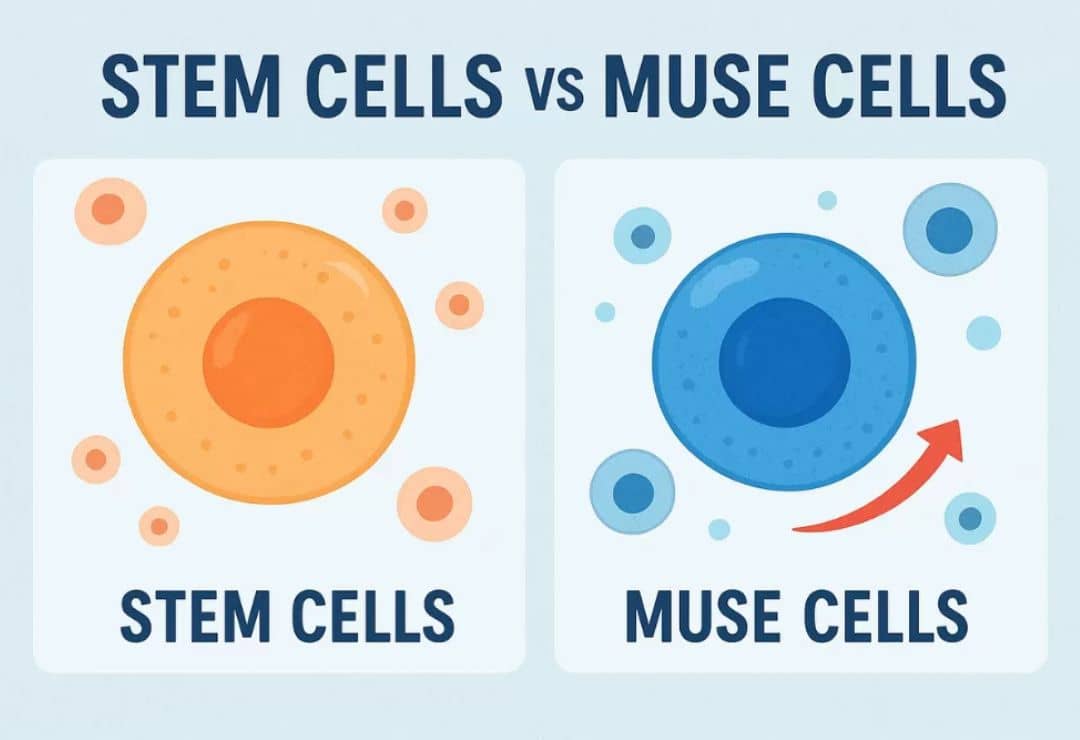
Stem Cells vs Muse Cells: While stem cells can differentiate into various cell types for regeneration, Muse cells are a unique subset with self-renewing and stress-tolerant properties. Muse cells offer safer, spontaneous repair without tumor risks, making them a next-generation regenerative option.
Stem cell science is one of the most exciting advances in modern medicine. These cells can repair damage, support healing, and even slow aging.
Among them, a special type called Muse cells has gained attention.
Muse cells are natural stem cells found in bone marrow, blood, and skin. What makes them unique is their ability to travel directly to injured areas and start repairing without extra preparation. They are stronger than regular stem cells and can survive stress inside the body.
In simple words: when it comes to stem cells vs Muse cells, normal stem cells need special handling, while Muse cells act as the body’s built-in repair team.
What Are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are the body’s master cells. They can develop into many different types of specialized cells, such as muscle, nerve, or skin cells. Because of this ability, stem cells are widely used in regenerative medicine to repair injuries, restore function, and promote healing.
Unveil Your Next Chapter With Dynasty
Our dedicated team is here to answer your questions and guide you on your path to well-being. Get in touch today to schedule a consultation or explore our services.
Types of stem cells include:
- Embryonic stem cells (ESCs): Pluripotent cells that can develop into any cell type.
- Adult stem cells (MSCs, HSCs, etc.): Found in bone marrow, fat, or blood, typically used for repair and regeneration.
- Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs): Adult cells reprogrammed to act like embryonic cells.
These cells are effective, but their use can sometimes raise ethical concerns, safety issues, or limitations in targeting specific damaged tissues.
What Are Muse Cells?
Muse cells (Multilineage-differentiating Stress-Enduring cells) are a special type of stem cell discovered more recently. Unlike regular stem cells, Muse cells are naturally found in adult tissues like bone marrow and fat. They are unique because they:
- Survive extreme stress: Muse cells resist harsh environments in the body.
- Home directly to damaged tissue: They naturally travel to injured or inflamed areas without external guidance.
- Differentiate into multiple cell types: Similar to other stem cells, they can become nerve, muscle, liver, or skin cells.
- Safe and non-tumorigenic: Unlike some stem cells, Muse cells do not form tumors, making them safer for medical use.
Muse cells act as the body’s built-in repair system, responding to injury and stress to restore balance and function.
Stem Cells vs Muse Cells: Key Differences
| Feature | Stem Cells | Muse Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Stem Cells (e.g., Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Embryonic Stem Cells) | Multilineage-differentiating Stress-Enduring Cells |
| Discovery | Known since early 20th century | Discovered in 2010 by Dr. Mari Dezawa’s team (Tohoku University, Japan) |
| Source | Found in bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord, etc. | Found within mesenchymal stem cell populations in bone marrow, fat, and skin fibroblasts |
| Stress Resistance | Sensitive to environmental stress and culture conditions | Highly stress-tolerant and survive extreme environments |
| Differentiation Ability | Can differentiate into specific lineages depending on type (e.g., mesoderm, ectoderm, endoderm) | Naturally pluripotent — can differentiate into all three germ layers without genetic manipulation |
| Tumor Formation Risk | Some stem cells (like embryonic) have a risk of tumor formation | No tumor formation observed — considered non-tumorigenic |
| Ethical Concerns | Embryonic stem cells raise ethical issues | No ethical issues — derived from adult tissues |
| Immunogenicity | May cause immune response depending on donor source | Immunologically privileged — low risk of immune rejection |
| Regenerative Ability | Promotes regeneration by differentiation and paracrine signaling | Directly repairs tissues, releases growth factors, and integrates into damaged areas |
| Applications | Used in regenerative medicine, tissue engineering, and research | Used in regenerative therapy for organs, neurodegenerative diseases, autoimmune disorders, and anti-aging treatments |
| Clinical Safety | Depends on stem cell type and purity | Demonstrated high safety in human clinical trials (Japan, EU) |
| Culturing & Expansion | Requires controlled lab conditions; may lose potency over time | Naturally stable and self-renewing under standard culture conditions |
Which Is Better? Stem Cells or Muse Cells?
Both traditional stem cells and Muse cells play an important role in regenerative medicine. However, Muse cells offer unique advantages because of their natural safety, ability to target damaged tissues directly, and resilience in stressful environments.
For many patients, Muse cells represent the next generation of regenerative solutions, offering faster, safer, and more reliable outcomes.
Muse Cells in Dynasty Clinic
Dynasty Clinic provides advanced regenerative solutions, including medical options using Muse cells, designed to help patients heal naturally. Specialists carefully evaluate each case and create personalized plans to restore health, energy, and balance.

Final Thoughts
The comparison of stem cells vs Muse cells highlights how regenerative medicine continues to evolve. Traditional stem cells built the foundation, while Muse cells are now paving the way for safer and more effective healing solutions.
If you are interested in learning how Muse cells can support your health, book a private consultation in Dynasty Clinic today.
Book an Appointment
It’s easy and free!